Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a stylesheet language used to describe the presentation of a document written in a markup language. Its most common application is to style web pages written in HTML and XHTML, but the language can be applied to any kind of XML document, including SVG and XUL.
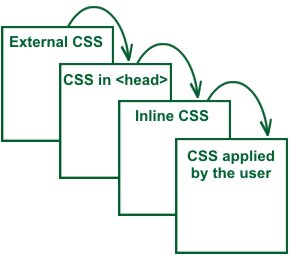
CSS can be used locally by the readers of web pages to define colors, fonts, layout, and other aspects of document presentation. It is designed primarily to enable the separation of document content from document presentation .This separation can improve content accessibility, provide more flexibility and control in the specification of presentation characteristics, and reduce complexity and repetition in the structural content. CSS can also allow the same markup page to be presented in different styles for different rendering methods, such as on-screen, in print, by voice and on Braille-based, tactile devices. CSS specifies a priority scheme to determine which style rules apply if more than one rule matches against a particular element. In this so-called cascade, priorities or weights are calculated and assigned to rules, so that the results are predictable.